Human Resource Management (HRM) is a vital function focused on managing an organization’s employees to achieve business success. It involves recruitment, employee benefits, and performance management, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and fostering a productive workforce. HRM plays a central role in maintaining employee relations, developing skills, and ensuring compliance with labor laws. Effective HR practices are essential for sustaining competitiveness in today’s dynamic business environment.
Importance of Human Resource Management in Organizations
Human Resource Management (HRM) is critical for organizational success, as it ensures effective utilization of human capital. By analyzing compensation trends, maintaining employment records, and facilitating professional development, HR experts drive employee growth and organizational performance. HRM also plays a key role in recruitment, employee benefits, and strategic planning, aligning workforce capabilities with business objectives. Additionally, HRM fosters positive employee relations, ensures legal compliance, and supports the creation of a productive work environment, ultimately contributing to the overall success and sustainability of the organization.
Key Functions of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) involves several critical functions, including recruitment, employee benefits, performance tracking, and legal compliance. HR professionals oversee administrative tasks such as coordinating compensation, maintaining employment records, and facilitating professional development. They also play a role in strategic planning, ensuring alignment of workforce capabilities with business objectives. Additionally, HRM includes managing employee relations, implementing training programs, and ensuring compliance with labor laws. These functions collectively contribute to creating a productive and efficient work environment, fostering employee growth and organizational success.

Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) involves aligning HR practices with business objectives to optimize organizational performance. It treats employees as valuable assets, focusing on long-term success and adaptability.
Aligning HR Strategies with Business Goals
Aligning HR strategies with business goals ensures organizational success by creating a cohesive approach to human capital management. HR leaders analyze industry trends and develop tailored strategies to meet specific business objectives, fostering alignment across all departments. This integration enhances employee engagement, productivity, and overall performance, driving the organization toward its long-term vision. By leveraging data-driven insights, HR strategies are optimized to support both employee and organizational growth, ensuring a competitive edge in the market.
Process of Strategic Human Resource Management
The process of Strategic Human Resource Management involves analyzing the organization’s mission and objectives, identifying required skills, developing strategies to attract and retain talent, implementing these through recruitment and training, and continuously monitoring and evaluating their effectiveness to ensure alignment with business goals.
Benefits of Implementing SHRM
Implementing Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) enhances organizational performance by aligning HR practices with business objectives. It improves efficiency, productivity, and decision-making by leveraging data-driven insights. SHRM fosters employee engagement, retention, and development, leading to a competitive edge. It ensures better resource allocation, reduces costs, and supports long-term sustainability. Additionally, SHRM promotes a culture of innovation and adaptability, enabling organizations to respond effectively to market changes. Ultimately, it strengthens the organization’s ability to achieve its mission and vision while maintaining a skilled and motivated workforce.
Recruitment and Selection Process
The recruitment and selection process involves attracting, evaluating, and selecting candidates to ensure the best fit for organizational roles, optimizing effectiveness and compliance.
Best Practices in Recruitment and Hiring
Effective recruitment involves a well-defined process, clear job descriptions, and diverse sourcing strategies to attract qualified candidates. Employers should use structured interviews, standardized evaluation criteria, and candidate assessments to ensure fairness and accuracy. Leveraging technology, such as applicant tracking systems, improves efficiency and transparency. Additionally, fostering a positive candidate experience enhances the employer’s brand. Ensuring compliance with equal employment opportunity laws and promoting diversity and inclusion are critical. Regular feedback and continuous improvement in the hiring process further optimize outcomes for both organizations and applicants.
- Clear job descriptions and person specifications.
- Diverse sourcing strategies to attract a wide talent pool.
- Structured interviews and standardized evaluation criteria.
- Use of assessments and skills testing where applicable.
- Regular feedback and continuous process improvement.
- Compliance with equal employment opportunity laws.
Role of AI in Recruitment and Selection
Artificial Intelligence (AI) significantly enhances recruitment efficiency by automating tasks like resume screening, candidate shortlisting, and interview scheduling. AI tools analyze candidate data to predict performance and cultural fit, reducing biases through data-driven decisions. Chatbots engage candidates, provide updates, and gather feedback, improving the hiring experience. Additionally, AI-powered systems ensure compliance with labor laws and diversity goals. These technologies streamline processes, enabling HR teams to focus on strategic roles while maintaining objectivity and scalability in recruitment. AI thus revolutionizes hiring, making it faster, precise, and candidate-centric.
- Automated resume screening and candidate shortlisting.
- Predictive analytics for candidate fit and performance.
- Chatbots for candidate engagement and communication.
- AI-driven interview scheduling and assessment tools.
- Data analysis for compliance and diversity goals.
Legal Considerations in Recruitment
Ensuring compliance with labor laws is crucial in recruitment to avoid legal disputes. Employers must adhere to anti-discrimination laws, such as Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, to prevent bias based on race, gender, religion, or other protected characteristics. Additionally, employers must verify the legal eligibility of candidates to work, comply with wage and hour laws, and ensure transparency in job postings. Proper handling of background checks and data privacy is also essential to maintain ethical hiring practices and protect both employers and candidates.
- Adherence to anti-discrimination laws.
- Verification of work eligibility.
- Compliance with wage and labor regulations.
- Transparency in job postings.
- Respect for candidate data privacy.
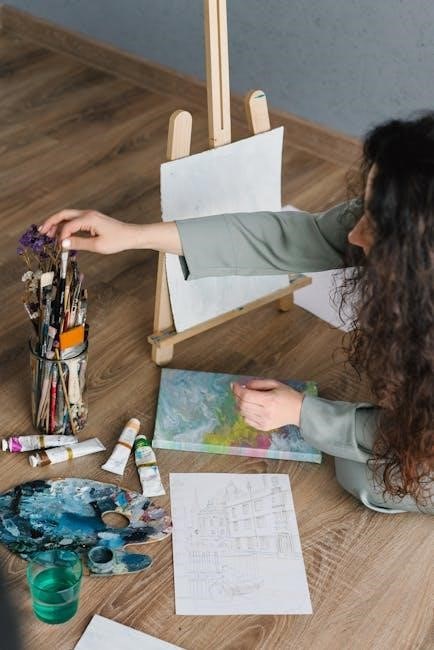

Employee Development and Training
Employee development and training are vital for enhancing skills, productivity, and job satisfaction. They ensure employees align with organizational goals and stay competitive in a changing work environment.
Types of Employee Training Programs
Employee training programs vary to meet organizational needs. Technical training enhances job-specific skills, while soft skills training focuses on communication and teamwork. Compliance training ensures legal adherence, and leadership development builds managerial capabilities. Onboarding programs acclimate new hires, and diversity and inclusion training fosters a respectful workplace. Continuous learning opportunities, such as upskilling and reskilling, prepare employees for future challenges. These programs ensure employees remain competitive, adaptable, and aligned with organizational goals, driving overall performance and growth.
Leadership Development Programs
Leadership development programs are designed to cultivate future leaders by enhancing critical skills like decision-making, strategic thinking, and communication. These programs often include mentorship opportunities, workshops, and 360-degree feedback to foster growth. They focus on aligning individual aspirations with organizational goals, ensuring a steady pipeline of capable leaders. Continuous learning and practical application of leadership principles are emphasized, preparing employees to handle complex challenges and drive innovation within the organization;
Impact of Training on Employee Performance
Training significantly enhances employee performance by improving skills, knowledge, and confidence. It empowers employees to execute tasks more efficiently, aligning with organizational objectives. Effective training programs lead to increased productivity, better decision-making, and higher job satisfaction. Additionally, trained employees demonstrate improved problem-solving abilities and adaptability to change. This directly contributes to reduced errors, enhanced innovation, and overall business growth. Continuous learning opportunities also foster employee engagement and retention, creating a more skilled and motivated workforce.
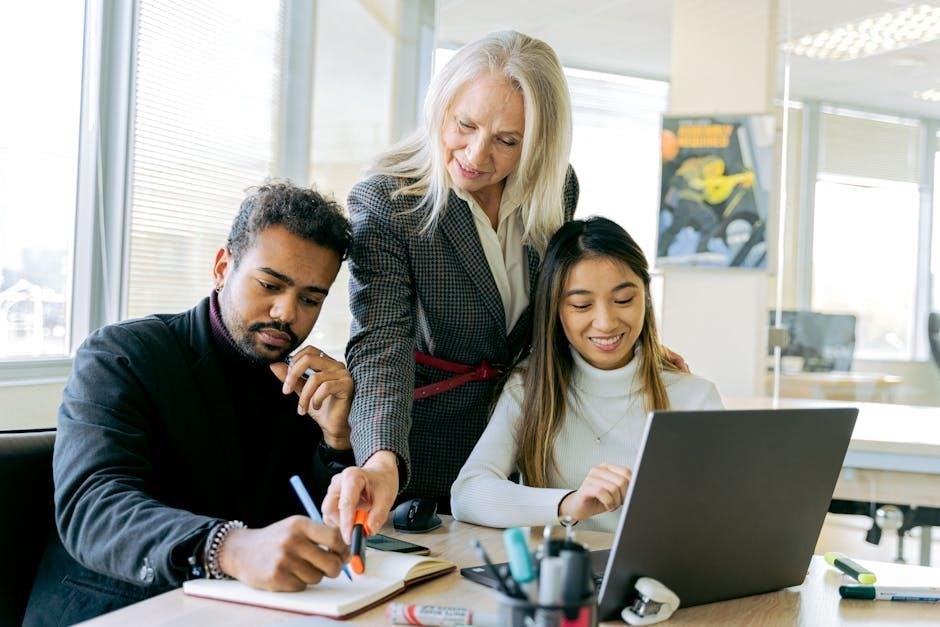

Employee Relations and Engagement
Building trust and communication fosters positive employee relations, enhancing collaboration and job satisfaction. Engaged employees are more productive, loyal, and committed to organizational success.
Building Positive Employee Relations
Building positive employee relations involves fostering trust, communication, and mutual respect within the workplace. Open dialogue, regular feedback sessions, and transparent policies help create a supportive environment. Recognizing employee contributions and celebrating milestones strengthens bonds. Employers should encourage collaboration, offer growth opportunities, and ensure fairness in treatment. Addressing grievances promptly and maintaining confidentiality also builds trust. Positive relations lead to increased morale, reduced turnover, and a more cohesive team. Effective communication and empathy are key to nurturing these relationships and fostering a positive organizational culture.
Strategies for Improving Employee Engagement
Improving employee engagement requires a multifaceted approach. Setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and recognizing achievements fosters a sense of purpose. Offering professional development opportunities, such as training and career growth, enhances motivation. Encouraging work-life balance and creating a positive workplace culture also boosts engagement. Empowering employees with autonomy and involving them in decision-making processes increases satisfaction. Celebrating milestones and fostering teamwork through collaborative activities further strengthens engagement. These strategies create a fulfilling work environment, leading to higher productivity and retention.
Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
Conflict resolution is crucial for maintaining harmony and productivity in organizations. Effective strategies include active listening, remaining neutral, and encouraging open communication. Mediation by HR or supervisors can help resolve disputes fairly. Training employees in conflict management skills, such as negotiation and emotional intelligence, prevents escalations. Clear policies and procedures ensure consistency in addressing issues. Fostering a culture of respect and collaboration minimizes conflicts and promotes a positive work environment. Addressing conflicts promptly reduces tension and enhances employee satisfaction and retention.
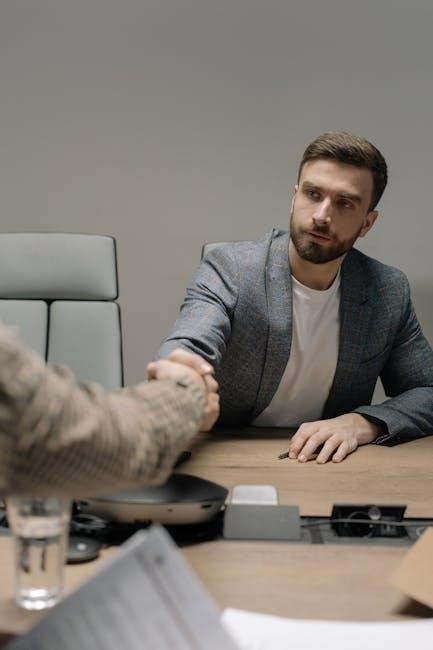

Compensation and Benefits Management
Compensation and benefits management ensures fair pay, motivates employees, and attracts talent. It involves designing salary structures, bonuses, and perks, aligning with legal and market standards while promoting equity and transparency to enhance employee satisfaction and organizational performance.
Designing an Effective Compensation Strategy
Designing an effective compensation strategy involves aligning pay structures with organizational goals, conducting market research, and balancing internal equity. It requires analyzing job roles, determining pay grades, and incorporating incentives to motivate performance. A well-designed strategy ensures transparency, competitiveness, and compliance with labor laws, fostering employee satisfaction and retention. Organizations must also consider cost constraints and long-term sustainability while tailoring compensation packages to meet diverse employee needs and drive business success.
Types of Employee Benefits and Their Importance
Employee benefits encompass health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, wellness programs, and professional development opportunities. These offerings enhance job satisfaction, improve work-life balance, and foster long-term loyalty. Health benefits address physical and mental well-being, while retirement plans ensure financial security. Paid leave and wellness programs boost productivity and morale. Professional development opportunities, such as training and education support, encourage growth and retention. Tailoring benefits to employee needs strengthens organizational culture and competitiveness in attracting talent.
Optimizing Compensation and Benefits Packages
Optimizing compensation and benefits packages involves aligning them with industry standards and employee expectations to enhance satisfaction and retention. Conducting market research and gathering employee feedback helps tailor offerings to meet diverse needs. Personalizing benefits, such as flexible plans, increases perceived value. Regularly reviewing and adjusting packages ensures they remain competitive and cost-effective. This balance supports organizational goals while fostering a motivated and loyal workforce. Additionally, transparent communication about the value of these packages can further enhance employee appreciation and engagement, leading to higher productivity.

Legal Aspects of Human Resource Management
Legal aspects of HR involve ensuring compliance with labor laws, promoting fairness, and preventing discrimination. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, damaging organizational reputation.
Understanding Labor Laws and Regulations
Labor laws and regulations govern employment practices, ensuring fairness and protection for both employers and employees. These laws cover wages, working hours, anti-discrimination, and workplace safety. Key legislations include the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the Civil Rights Act, which prohibit discrimination based on race, gender, or disability. Compliance with these laws is critical to avoid legal penalties and promote a just work environment. HR professionals must stay updated on evolving regulations to ensure adherence and safeguard employee rights effectively.
Ensuring Compliance in HR Practices
Compliance in HR involves adhering to labor laws, regulations, and organizational policies to maintain legal and ethical standards. HR teams must conduct regular audits, training sessions, and policy updates to ensure adherence. Documentation of employee records, contracts, and grievance procedures is crucial. Compliance fosters a fair workplace, minimizes legal risks, and enhances organizational reputation. Staying informed about regulatory changes and implementing robust monitoring systems are key to maintaining compliance effectively across all HR functions and processes.
Managing Data Privacy in HR
Managing data privacy in HR ensures the protection of sensitive employee information, such as personal details, salaries, and health records. Organizations must comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA to safeguard data. HR teams implement access controls, encryption, and secure storage systems. Regular audits and employee training on data handling are essential. Limiting data access to authorized personnel and ensuring transparency in data usage builds trust and prevents breaches. Privacy management is critical for maintaining ethical standards and legal compliance in HR practices.

Technology in Human Resource Management
Technology enhances HR efficiency by automating tasks, improving data analysis, and enabling better decision-making. It supports employee engagement, performance tracking, and streamlined communication across organizations.
Role of HR Information Systems (HRIS)
HRIS streamlines HR processes by automating tasks like payroll, attendance, and performance tracking, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. It enables centralized data management, improving decision-making through analytics and reporting. HRIS also supports compliance by ensuring accurate record-keeping and data security. Integration with other systems, such as CRM or accounting software, further enhances operational alignment. Additionally, HRIS provides self-service portals for employees, fostering transparency and empowerment. Overall, HRIS is a critical tool for modern HR, driving productivity and strategic alignment within organizations.
AI and Automation in HR Processes
AI and automation revolutionize HR by streamlining repetitive tasks, such as resume screening, interview scheduling, and payroll processing. AI-powered tools enhance decision-making with predictive analytics, identifying top candidates and forecasting employee turnover; Chatbots provide instant support for employee queries, improving engagement. Automation ensures consistency in performance evaluations and compliance with labor laws. Additionally, AI-driven systems personalize employee learning paths and optimize talent acquisition, enabling HR to focus on strategic initiatives. This integration enhances efficiency, accuracy, and employee experience, driving modern HR practices forward.
Impact of Remote Work Technologies on HR
Remote work technologies significantly influence HR practices, enabling seamless communication and collaboration. Tools like Slack and Zoom facilitate team connectivity, while platforms like Trello and Asana streamline task management. HR can monitor productivity and engagement through digital dashboards. Remote work technologies also enhance employee experience by fostering flexibility and work-life balance. However, HR must address challenges like data security, compliance, and ensuring equitable access to tools. These technologies redefine workforce management, emphasizing the need for adaptable HR strategies to support remote teams effectively.

Global Human Resource Management
Global HRM involves managing diverse workforces across countries, addressing cultural differences, legal requirements, and coordination challenges. It ensures alignment of HR practices with global business goals while fostering collaboration and inclusivity across borders.
Challenges of Managing a Global Workforce
Managing a global workforce presents unique challenges, including cultural differences, language barriers, and varying legal regulations. Coordinating across time zones and balancing standardized HR practices with local norms can be complex. Additionally, geopolitical instability, expatriate management, and ensuring diversity and inclusion across borders require strategic attention. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for fostering collaboration and maintaining organizational cohesion in a globalized business environment.
Cultural Factors in International HRM
Cultural factors significantly influence international HRM, as differences in values, beliefs, and practices shape workplace behaviors. HR professionals must navigate variations in communication styles, decision-making norms, and attitudes toward hierarchy. Understanding cultural dimensions, such as individualism vs. collectivism, helps tailor policies to local contexts. Additionally, cultural sensitivity is crucial for building trust and ensuring inclusive practices. Effective cross-cultural training and adaptability are essential for fostering collaboration and productivity in diverse global teams, aligning HR strategies with cultural nuances.
Managing Expatriates in Global Organizations
Managing expatriates in global organizations involves selecting, training, and supporting employees for international assignments. Cultural adaptation and language skills are critical for success. Organizations must provide pre-departure training, relocation assistance, and ongoing support to address challenges like homesickness and family adjustment. Compensation packages often include allowances for cost of living and housing. Legal and tax considerations must also be addressed to ensure compliance. Effective expatriate management enhances global operations and fosters organizational growth by leveraging diverse talent effectively.

Future Trends in Human Resource Management
Future trends in HRM include embracing remote work, focusing on personalized employee experiences, leveraging advanced analytics, prioritizing diversity and inclusion, and investing in continuous upskilling initiatives.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on HR
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing HR by automating tasks like recruitment, payroll, and performance tracking. AI tools enhance decision-making through predictive analytics, enabling better hiring choices and employee retention strategies. Chatbots and virtual assistants improve employee engagement by providing instant support. Personalized learning platforms powered by AI cater to individual development needs. However, ethical concerns like data privacy and bias in AI algorithms must be addressed to ensure fair and transparent HR practices. AI is reshaping HR into a more efficient and data-driven function.
Focus on Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) are critical for fostering inclusive workplaces where all employees thrive. HR plays a pivotal role in promoting DEI by implementing policies that ensure equal opportunities, unbiased hiring practices, and inclusive cultures. Training programs and diversity initiatives help address unconscious biases and create a sense of belonging. Equitable access to resources and opportunities ensures fairness for all employees. By prioritizing DEI, organizations enhance innovation, employee satisfaction, and retention while aligning with societal expectations for inclusivity and social responsibility.
Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility in HR
Sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) are integral to modern HR practices, ensuring organizations contribute positively to environmental and social well-being. HR departments play a crucial role in implementing green workplace policies, promoting ethical labor practices, and fostering a culture of responsibility. By aligning HR strategies with CSR goals, organizations can enhance their reputation, support long-term environmental and social well-being, and encourage employee engagement in sustainable practices, ultimately benefiting both the business and society.
Human resource management is vital for aligning organizational goals with employee well-being, fostering growth, and driving sustainable success in a dynamic business environment.
Key Takeaways from Human Resource Management
Effective human resource management is crucial for optimizing organizational performance and employee satisfaction. It involves strategic planning, recruitment, development, and fostering positive workplace relations. HR practices must align with business objectives, ensuring compliance with labor laws and adapting to technological advancements. By prioritizing employee engagement, diversity, and continuous learning, organizations can build a resilient and motivated workforce. Ultimately, HRM plays a pivotal role in driving long-term success, sustainability, and innovation in a competitive and evolving business landscape.
Evolution and Future of HRM
Human Resource Management has evolved from administrative roles to strategic partnership in organizational success. The shift focuses on leveraging technology, fostering diversity, and addressing global challenges. Future trends include AI-driven analytics, personalized employee experiences, and sustainability initiatives. HR will prioritize upskilling, mental health, and remote work integration. Embracing innovation and ethical practices will define HRM’s role in shaping resilient, inclusive organizations. The future demands adaptability, aligning HR strategies with societal and technological advancements to drive sustainable growth and employee well-being.



